Workforce Identity Management Capabilities
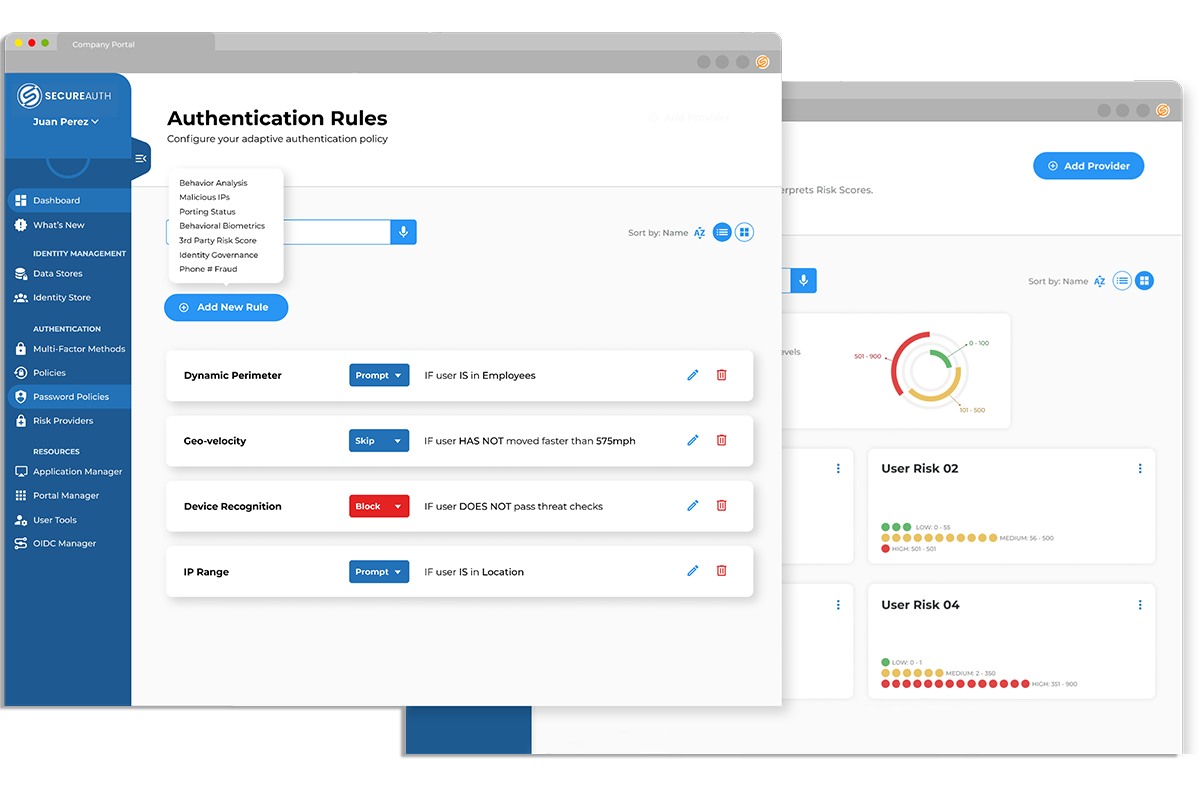
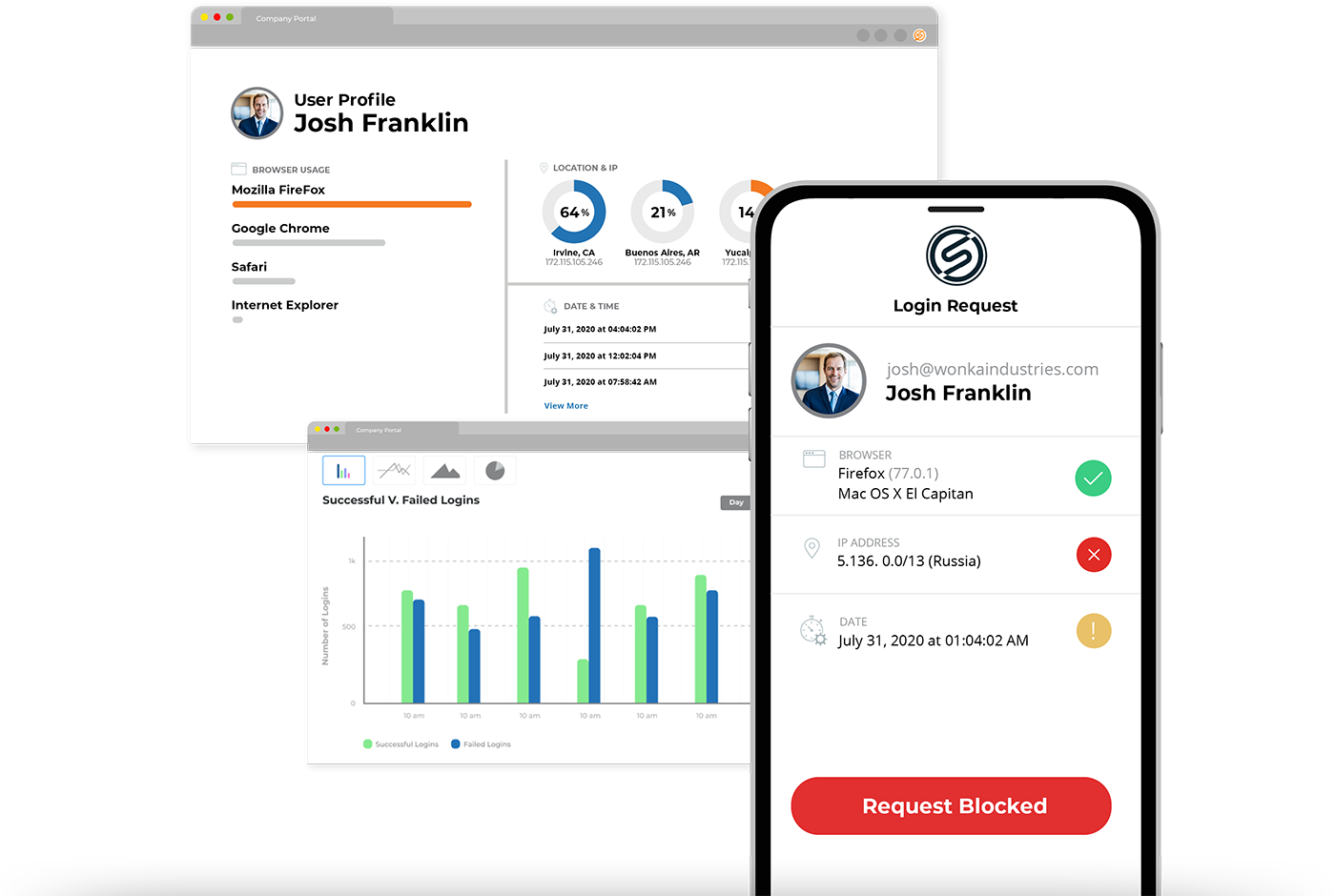
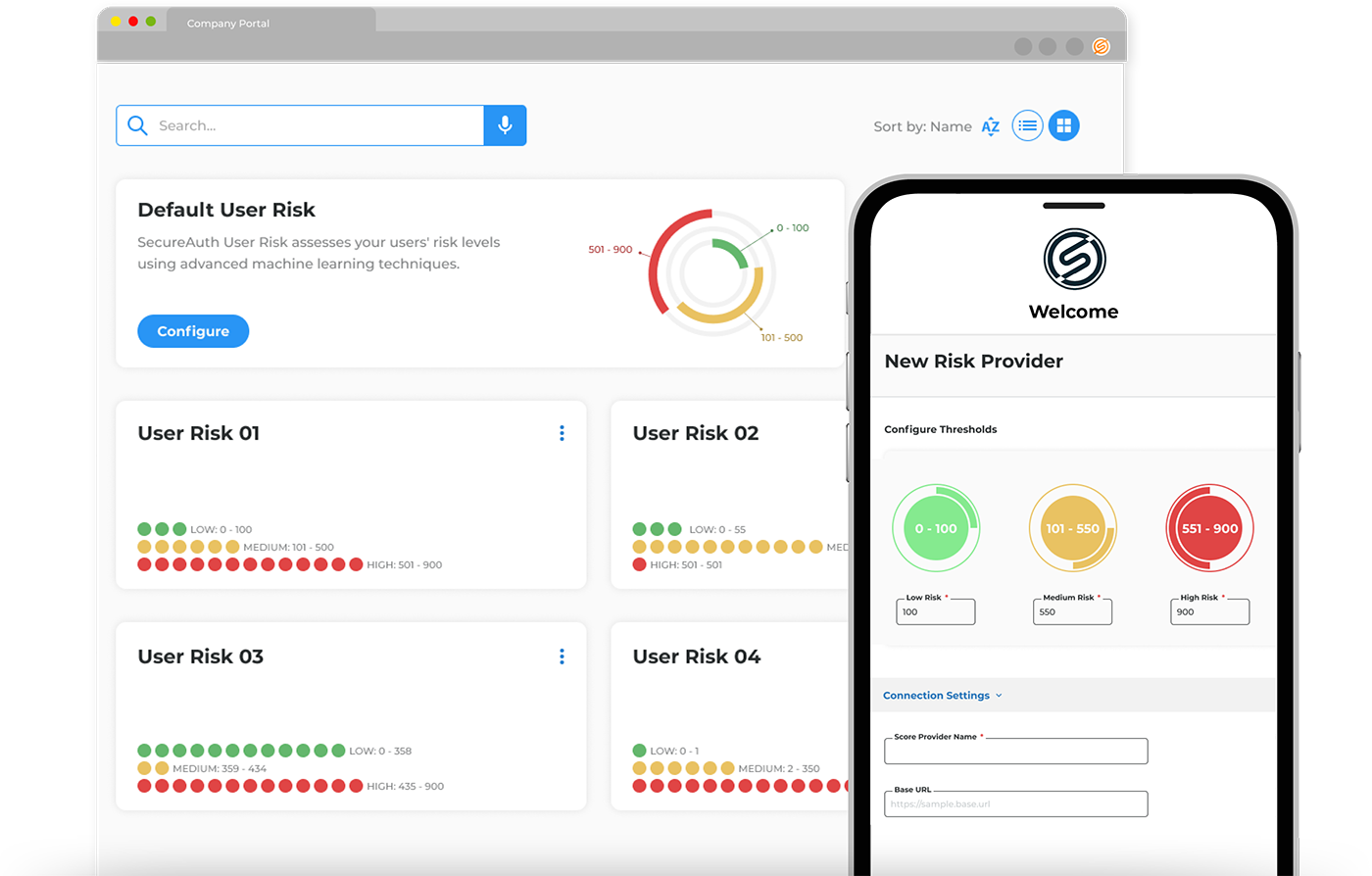
Adaptive Authentication
Why adaptive authentication capabilities matter for better workforce identity management.
For your employee
“I like that I only have to provide additional log-in information when I am doing something unusual like working from a different location or using a different device.”
For your company
“Our company assigns different risk tolerances for different systems and behaviors ensuring that we can balance security and the user experience for our employees.”

Related Resources
REPORT
Passwordless Access & Adaptive Authentication
REPORT
Workforce Identity Management Overview
REPORT