As organizations navigate the complexities of the digital age, securing user access while maintaining seamless experiences has become a paramount challenge. Our research in our 2024 State of Authentication Report, based on a survey of IT and security professionals, shows that businesses are at a critical juncture in how they manage identity and access. This article distills key insights from the report to offer CIOs actionable strategies to enhance their security posture and capitalize on emerging trends.
1. The Rise of Authentication as a Top Priority

84% of respondents ranked authentication and access management among their top five cybersecurity priorities. This is no surprise, as credential-based attacks continue to dominate the threat landscape. Organizations must rethink their strategies to not only protect against these attacks but also create a secure and user-friendly experience.
Actionable Insight: Prioritize investigating advanced authentication technologies, such as passwordless and multi-factor authentication (MFA) solutions, which are less susceptible to breaches. Adopting a continuous authentication approach can help detect and mitigate threats in real-time, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Traditional MFA: The Past or the Present?
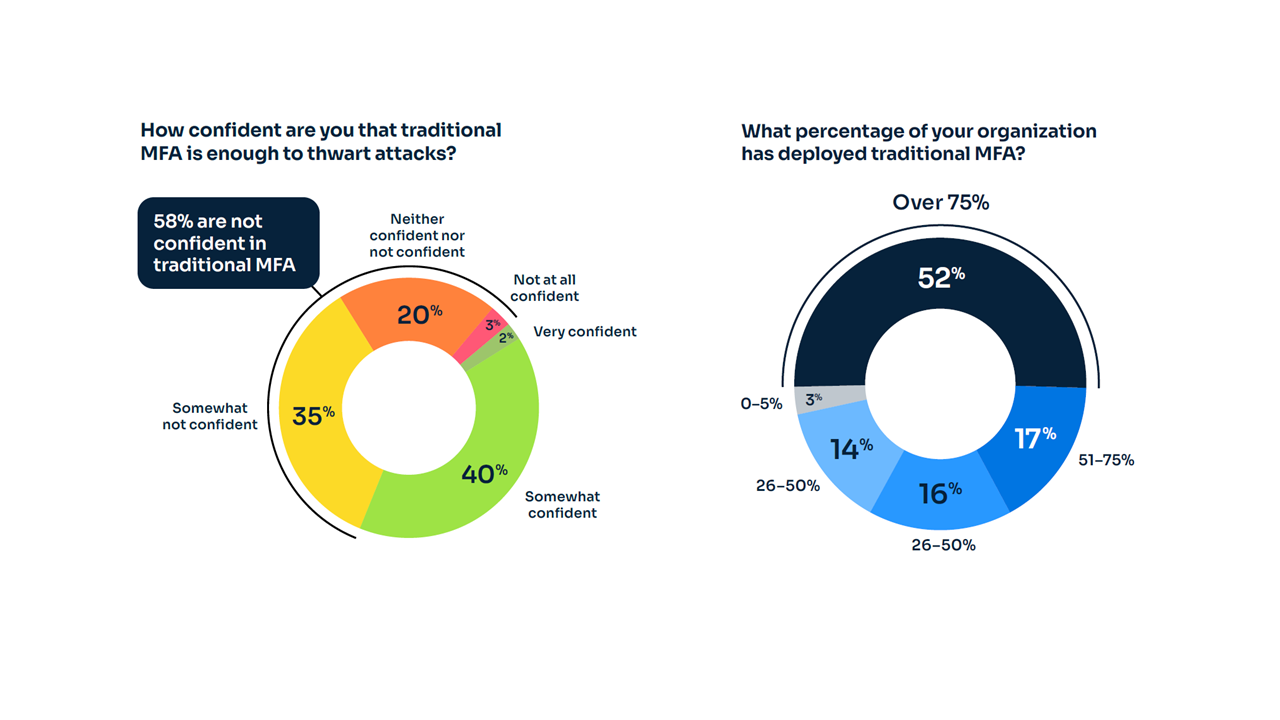
While MFA adoption has gained traction, the report notes that traditional MFA methods, such as SMS-based one-time passwords (OTPs) and PINs, are increasingly viewed as vulnerable. Over 58% of survey respondents expressed concerns about the susceptibility of these methods to cyberattacks, such as MFA bombing and man-in-the-middle attacks. Yet, over 50% of organizations have deployed traditional MFA to at least 75% of their users.
Actionable Insight: Consider phasing out traditional MFA methods in favor of phishing-resistant MFA or passwordless solutions. Phishing-resistant technologies, such as FIDO2-based authentication, provide greater security and a smoother user experience. CIOs should also work closely with security teams to reduce friction by implementing technology where authentication happens in the background, reducing the burden on users while strengthening security.
3. The Move to Passwordless: A Strategic Imperative
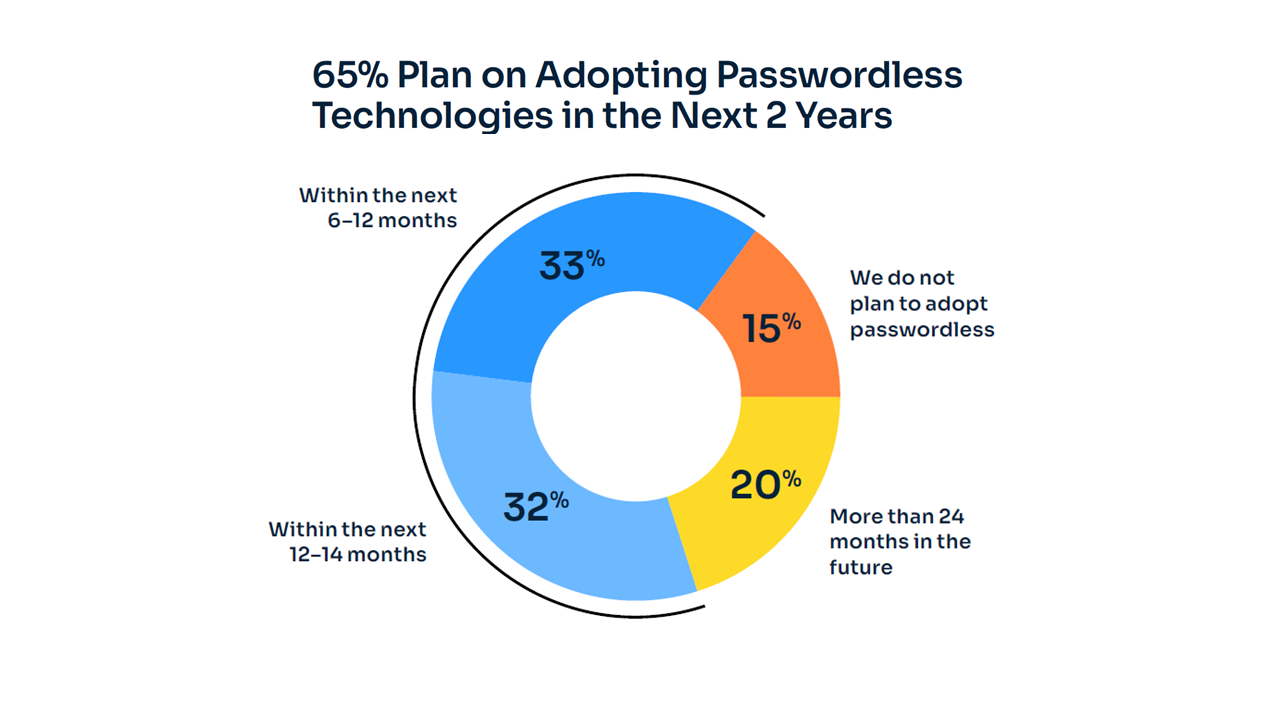
One of the most promising trends revealed in the report is the growing shift toward passwordless authentication, with 65% of organizations planning to adopt these technologies within the next two years. This transition is driven by the desire to eliminate weak points associated with passwords while improving the user experience.
However, the report also outlines key challenges to this adoption. Competing priorities, lack of knowledge about the technologies, and budget constraints were the most significant barriers to implementation, with 55% citing competing priorities as their primary challenge.
Actionable Insight: CIOs should develop a clear roadmap to passwordless adoption. Start with pilot programs for critical systems and high-risk users before scaling the implementation across the enterprise. Additionally, fostering education and awareness around the benefits of passwordless authentication can help overcome internal resistance. A phased approach can ensure budget alignment and stakeholder buy-in.
4. Multiple Identity Providers: A Necessary Complication

An intriguing finding from the report is that 76% of organizations use multiple identity providers (IdPs). This goes against the typical cybersecurity trend of consolidating tools, but the reasons are practical—failover capabilities, diverse use case requirements, and a preference for a best-of-breed approach. However, managing multiple IdPs increases administrative complexity and can introduce gaps in security.
Actionable Insight: Conduct a comprehensive audit of identity providers to assess the necessity of each platform. Where possible, consolidating IdPs can reduce administrative overhead and improve the efficiency of access management. If multiple providers are unavoidable, implementing a unified identity governance and administration solution can streamline the management of user identities and reduce the risk of unauthorized access across systems.
5. Device Trust: A Critical Yet Underutilized Tool
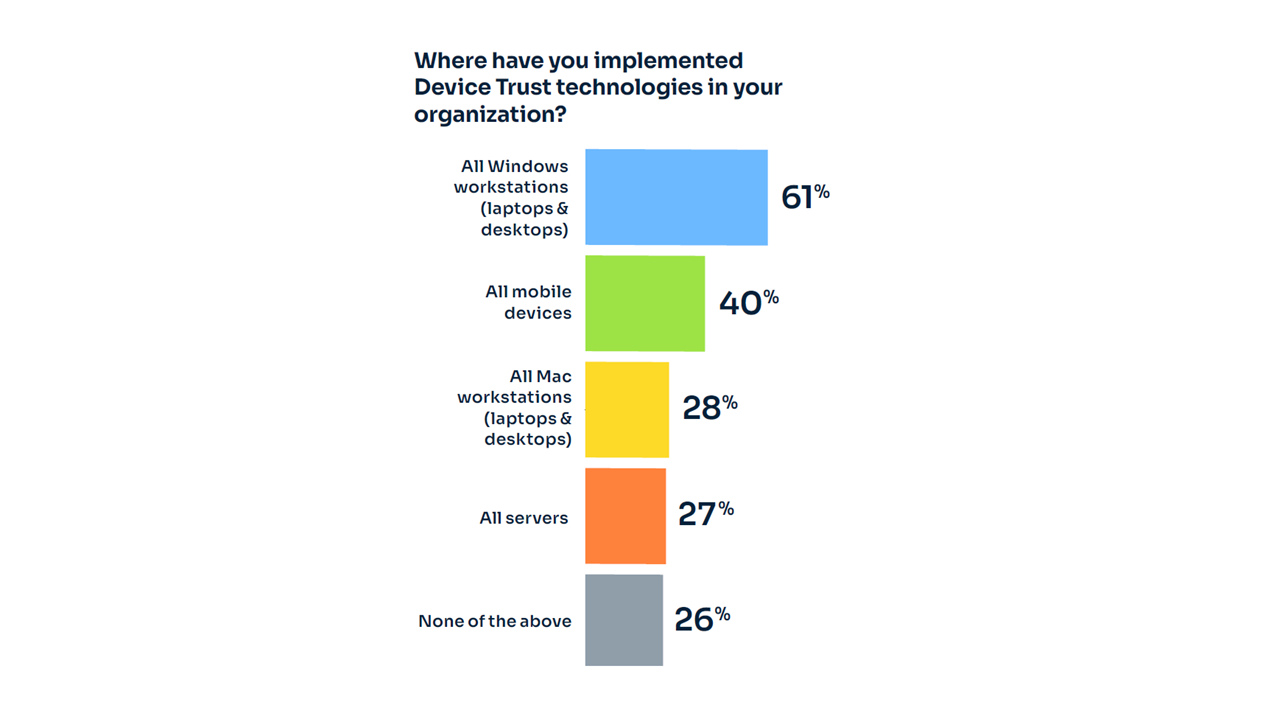
According to the report, device trust technologies remain underutilized, with only 40% of mobile devices and 28% of Mac workstations employing these solutions. Device trust plays a pivotal role in securing the user’s digital journey, particularly in a remote and hybrid work environment. Without device trust, even robust MFA systems can be vulnerable to attacks where credentials are stolen.
Actionable Insight: Device trust technology deployment cannot be an afterthought, especially for mobile and remote workers. These technologies enable organizations to monitor device characteristics, such as geolocation and keystroke patterns, to ensure the legitimacy of the user attempting to access sensitive resources. Integrating device trust with existing MFA and authentication systems can enhance security without compromising user experience.
6. The Growing Role of Cyber Insurance in Authentication
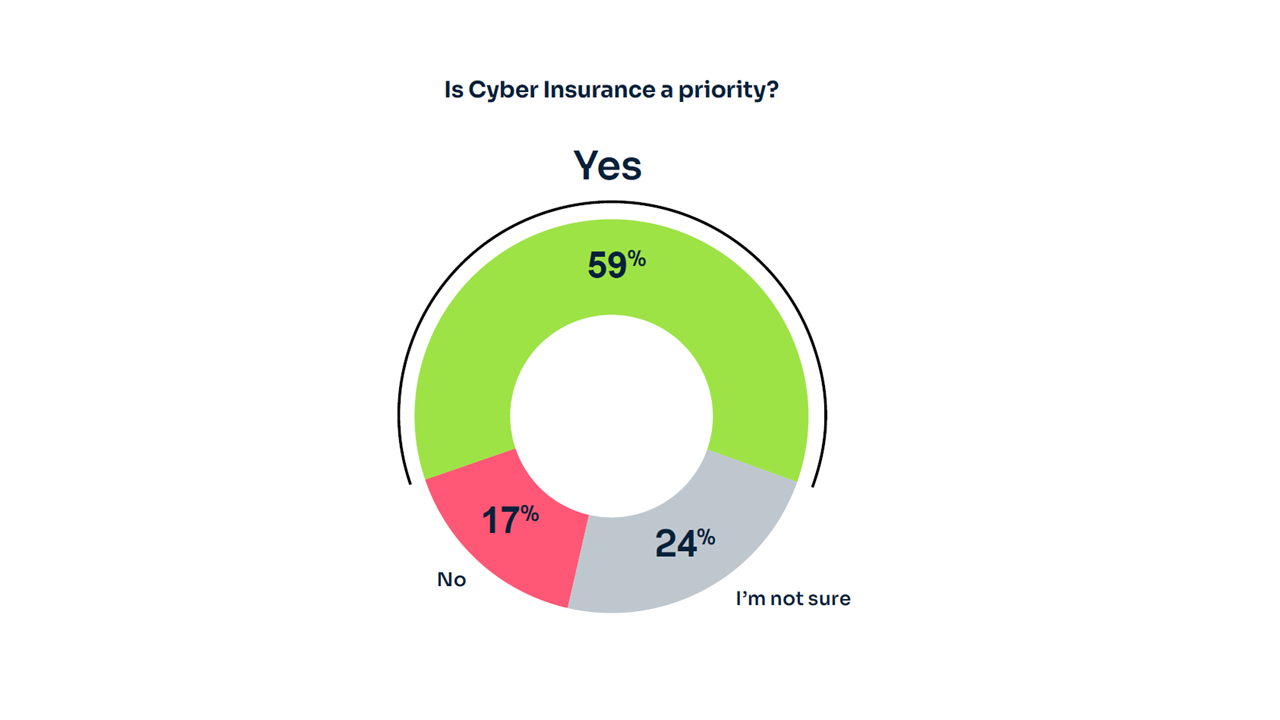
As cyber insurance becomes a staple for managing residual cyber risk, the report notes that 59% of respondents view it as a priority. However, insurers are increasingly mandating stronger authentication controls as a prerequisite for coverage. This shift signals a need for organizations to adopt more advanced MFA solutions to secure favorable insurance terms.
Actionable Insight: CIOs should proactively review their cyber insurance policies to understand the authentication requirements needed to maintain or improve coverage. Collaborating with the organization’s risk management team can ensure that the adoption of modern authentication technologies meets these evolving requirements.
7. Invisible MFA: The Future of Seamless Security

The concept of invisible MFA, where authentication takes place without disrupting the user experience, is gaining traction. According to the report, 35% of respondents are prioritizing risk-based continuous authentication—a form of invisible MFA that monitors user behavior and adapts security measures accordingly. This approach not only enhances security but also reduces user friction, a key pain point in traditional authentication methods.
Actionable Insight: Explore the use and integration of this technology into current security architecture to reduce the reliance on user intervention, improving both security and productivity. Implementing contextual authentication, which assesses the risk of each login attempt based on user behavior, location, and device, can provide an additional layer of protection while keeping the user experience seamless.
A Call to Action for CIOs
The findings from our 2024 State of Authentication Report reveal that while traditional methods of authentication remain prevalent, they are no longer sufficient to combat today’s sophisticated cyber threats. As CIOs, it is imperative to stay ahead of these trends by adopting advanced approaches. Identity solutions are typically pretty sticky, with an average tenure of 7-10 years. One of the main barriers to adopting new solutions is the perception that implementing them requires a lengthy, multi-year project. However, there are now options that allow you to unify all users under a single identity experience within weeks, while backend consolidation of IAM stacks happens over time. Don’t let the fear of a long project prevent your organization from exploring better, more efficient identity solutions. By prioritizing these innovations, CIOs can not only improve their organization’s security posture but also reduce user friction, drive operational efficiencies, and ensure compliance with evolving cyber insurance mandates.
Download your copy of the report today.
